Mandatory medical examinations and vaccines ensure good health, growth and psychomotor development from an early age. There are about twenty of them, essential during the child’s first six years.
What you need to know:
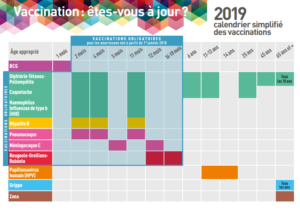
Medical examinations are not only about visits and controls, in fact, compliance with the schedule of mandatory vaccines is just as important according to age:
Source: vaccination-info-service
Mandatory vaccines since 2018:
- Diphtheria
- Tetanus
- Poliomyelitis
- The whooping cough
- Haemophilus influenzae b
- Meningococcus C
- The Pneumococcus
- Measles
- The Mumps
- The Rubella
These vaccines are mandatory before the age of 2 years for infants born on or after 1 January 2018. For children born before this date, vaccinations against Diphtheria, Tetanus and Poliomyelitis are mandatory at 2, 4 and 11 months of age. Finally, for Guyanese children in France, vaccination against yellow fever is compulsory.
Medical examinations and controls:
From 0 to 6 months, vigilance and monitoring:
Of course, during the birth, the baby is carefully examined to prevent any anomalies (respiratory, cardiac…). However, we must not forget the 8th day examination, complete check-up (hearing, vision, neurology…) and above all the “Guthrie blood test” screening for five rare diseases:
- Phenylketonuria
- Congenital hypothyroid
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Sickle cell disease
- Cystic fibrosis
An examination during baby’s second week is also mandatory. During the first six months, a monthly medical check-up, which will aim to check the child’s health and carry out mandatory vaccinations.
From 6 to 12 months, quarterly follow-up:
Three visits are mandatory for this age group: 6, 9 and 12 months. The 9th month visit is very important, as it allows the doctor to complete a medical certificate at the Maternal and Child Protection Services (PMI). In addition, the doctor is much more attentive to the child’s hearing and vision. It performs “sensory baby-test” tests and controls reactions to low and high frequencies. The visit of the 12th month and she, a “linguistic” and “motor” check-up, in fact, these are the first words and no baby.
From 1 to 2 years, followed every four months:
Three visits are mandatory: 16, 20 and 24 months. These are lambda controls (weights, sizes, feeds…), however, it is also an opportunity to practice the different vaccines for these ages. In addition, the doctor supervises, at the age of 16 months, if the walk is well installed and at 20 months the child must be able to cross obstacles (stairs…). Finally, at 24 months, a new medical certificate is sent to the PMI with the same controls (auditory, visual and psychomotor).
After 2 years, followed every six months:
The purpose of these visits is to regularly monitor the child’s progress (BMI, language, sight, hearing, socialization, learning…).
Connected patch thermometers such as Tucky allow you to monitor your children’s temperature remotely. As well as to organize a health record so as not to forget these small tests and vaccines.
Tucky allows you to prevent small diseases or viruses and react as quickly as possible.
Sources :
- https://vaccination-info-service.fr/
- https://www.service-public.fr/particuliers/vosdroits/F967
- https://www.passeportsante.net/fr/Maux/examens-medicaux-operations/Fiche.aspx?doc=test-guthrie
- https://www.parents.fr/bebe/sante/examens-medicaux/sante-bebe-les-examens-medicaux-obligatoires-13772